Pollution has now become the threat for humans as well as to the environment, the entire world is struggling and fighting against it and more than 50% percent of Pollution Around the world is because of vehicles. For tackling this issue European Standards of emission was introduced but around the world people still not aware with the term of EURO while in Many under developed countries people consider EURO as the term for increase engine performance & efficiency but they don’t know what is the core Purpose of EURO Engines and How they are Helping Humans.
Before digging deep first it is important to know that EURO engine doesn’t only mean that it will provide better performance or fuel efficiency but the major purpose is to reduce pollution emission into the environment. EURO Stands for European exhaust emission standards which are the legal requirements related to air pollution into atmosphere and should be followed by vehicle manufactures especially in European countries. Now not only the European countries but all countries around the world following it and making EURO (Emission control Standards) compulsory to follow as in India and Pakistan these rules are still not much applicable that is why people are not much aware of these standards.
What Does European Emissions Standards do?
Emissions Standards are made to set limits on the air pollution from vehicles because according to details more than 70% of pollution in cities is because of vehicles while according to 2014 DEFRA report 50 percent of all Urban Nox (Nitrogen oxide) is from petrol cars equipped with 1-3 EURO Technology.
When Does EURO Standards come into Law? :
First ever emissions standards were enacted in 1963 in united states that was made in response to Los Angeles smog problems while following it Japan enacted their emissions rules 3 years later and from 1970 to 1972 several other European nations start working on these and finally the 1stever EURO-I standards were set in 1992 which were applicable on passenger cars and light trucks.
- EURO-II (1996) = for passenger cars & for motorcycles
- EURO-III (2000) = for any vehicle and For Motorcycles
- EURO-IV (2005) = for any vehicle
- EURO-V (2009) = for light passenger and commercial vehicles
- EURO-VI (2014) = for light passenger and Commercial vehicles
European emission standards are not applicable on ships and aeroplanes but obviously their manufacturers are also working to decrease pollution in the environment.
How Manufactures Achieve EURO Emission Standards:
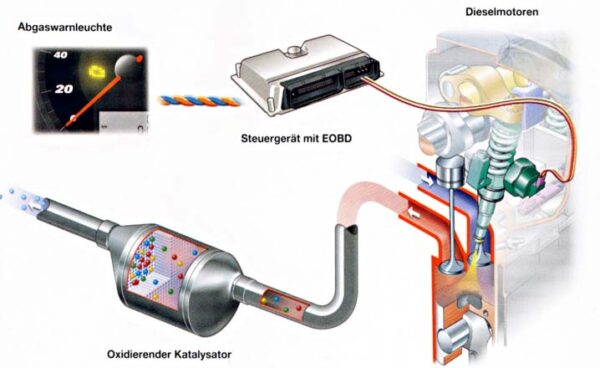
For controlling the emissions of toxic gases manufactures come up with catalytic converter which is an exhaust emission control device that most commonly applied to exhaust system in automobiles. Catalytic converter reduces toxic gases by converting them into less toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redux reaction (and oxidation and a reduction reaction). In the beginning two ways catalytic converter were used to produce carbon dioxide and H2O by combing and converting oxygen with carbon monoxide and un-burned hydrocarbons but later on three way catalytic converters being made that were also reduces the oxides of Nitrogen.
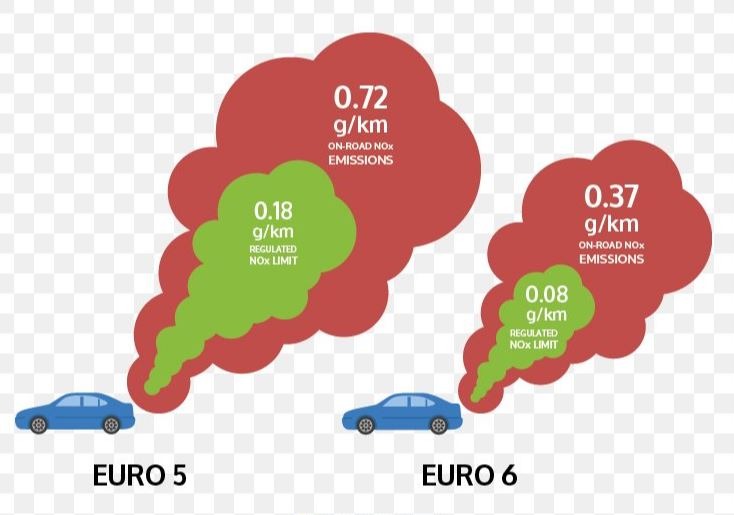
How Much Reduction made with Euro Emission standards up to EURO-6:
From 2014 to onward all manufactures around the world are following EURO-VI(6) standards while in Pakistan we still have Euro-II(2) vehicles but in recently new developed auto policy manufacturers are obligate to follow minimum EURO-IV(4) Emission standards.
Emissions Controlled with EURO Engines:
- Euro 1 emission standards (petrol)
- CO: 2.72g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.97g/km
- Euro 1 emission standards (diesel)
- CO: 2.72g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.97g/km
- PM: 0.14g/km
- Euro 2 emissions standards (petrol)
- CO: 2.2g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.5g/km
- Euro 2 emissions standards (diesel)
- CO: 1.0g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.7g/km
- PM: 0.08g/km
- Euro 3 emissions standards (petrol)
- CO: 2.3g/km
- THC: 0.20g/km
- NOx: 0.15g/km
- Euro 3 emissions standards (diesel)
- CO: 0.66g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.56g/km
- NOx: 0.50g/km
- PM: 0.05g/km
- Euro 4 emissions standards (petrol)
- CO: 1.0g/km
- THC: 0.10g/km
- NOx: 0.08g/km
- Euro 4 emissions standards (diesel)
- CO: 0.50g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.30g/km
- NOx: 0.25g/km
- PM: 0.025g/km
- Euro 5 emissions standards (petrol)
- CO: 1.0g/km
- THC: 0.10g/km
- NMHC: 0.068g/km
- NOx: 0.06g/km
- PM: 0.005g/km (direct injection only)
- Euro 5 emissions standards (diesel)
- CO: 0.50g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.23g/km
- NOx: 0.18g/km
- PM: 0.005g/km
- PN [#/km]: 6.0×10 ^11/km
- Euro 6 emissions standards (petrol)
- CO: 1.0g/km
- THC: 0.10g/km
- NMHC: 0.068g/km
- NOx: 0.06g/km
- PM: 0.005g/km (direct injection only)
- PN [#/km]: 6.0×10 ^11/km (direct injection only)
- Euro 6 emissions standards (diesel)
- CO: 0.50g/km
- HC + NOx: 0.17g/km
- NOx: 0.08g/km
- PM: 0.005g/km
- PN [#/km]: 6.0×10 ^11/km
Other Benefits of EURO Engines:
Not only the Euro Engines reduces pollutant gases like carbon, nitrogen or other hydrocarbons but with tighten of standards over the years and while following the Euro standards manufactures become able to produce more fuel efficient and Cost efficient engines.
Will Catalytic Converter remain there?
In upcoming future less and less vehicles will use catalytic converters as most of the countries around the world has set the policies to produce electric cars instead of gasoline and diesel so form 2024 to onward more than 50 percent of vehicles will be electric and most of the automakers already manufacturing environment friendly electric cars.
How cars tested for Emissions:
To make emission tests more reflective of real world WLTP (world harmonies light vehicle testing protocol) being introduced in 2018 that replaced NEDC tests. These tests also include additional real world driving emissions tests to detect regulated pollutant emissions.